Triethylene Glycol (TEG)
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Triethylene Glycol (TEG) (CAS 112-27-6) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Triethylene Glycol (TEG)
Chemical Name:Triethylene Glycol;TEG;CAS 112-27-6
EINECS No.: 203-953-2
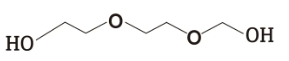
Chemical Formula: C6H14O4
Molecular Weight: 150.17
Melting point: -7°C
Boiling point: 125-127℃
Flash point: 165°C
Density (20 °C): 1.124 g/mL
Molecular Structure:
Description
Triethylene Glycol (TEG) is a colorless liquid with a mild odor and is denser than water. It is a member of a series of dihydroxyalcohols. TEG's primary applications are derived from its ability to absorb moisture. It is utilized as a dehydrating agent in natural gas pipelines to eliminate water from the gas before reusing it in the system. Triethylene glycol also has mild disinfectant qualities and, when volatised, is used as an air disinfectant for virus and bacteria control.
Triethylene Glycol (TEG) Standard
Appearance: Clear very slightly yellow viscous liquid
Content %≥: 99.5
Density (20 °C):: 1.124 g/mL
Vapor Pressure (20 °C): <0.01 mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.455
Explosive Limit %(V): 0.9-9.2
Application
1. Triethylene Glycol (TEG) plays a crucial role in the Oil & Gas industry, primarily leveraging its hygroscopic properties. The main applications in this sector include: TEG serves as a highly effective dehydrating agent in natural gas pipelines. It absorbs moisture from the air, removing water from the gas before condensation. This process prevents the gas from freezing, ensuring easier transportation and management for end consumers.
2. TEG is commonly employed as a mild disinfectant for air in occupied areas. Its low toxicity, antimicrobial properties, and subtle odor make it suitable for use in environments where more aggressive disinfectants may not be feasible. TEG’s disinfectant properties, combined with its dehydrating characteristics, make it an ideal choice as a dehumidifying agent in air-conditioning units. It helps maintain a comfortable and sanitized indoor environment.
3. It is used in fabric conditioning treatments to help maintain the softness and manageability of textiles. TEG can act as a lubricant in the spinning of fibers, aiding in the production of smoother, less tangled yarns. In textile printing, TEG can be used as a solvent to create inks and dyes that have the desired consistency and application properties.
4. Triethylene Glycol (TEG) is commonly used in the production of resins. TEG is a key component in the manufacturing of polyester resins. TEG is used in the production of alkyd resins, which are widely employed in the formulation of paints, coatings, and varnishes. Alkyd resins provide durable and glossy finishes in various applications.
5. TEG serves as a soluble solvent in the formulation of chemical adhesives and fillers. TEG is employed as an absorber in various processes, contributing to its effectiveness in specific industrial applications. TEG finds use in the formulation of fuels and fuel additives, contributing to their properties and performance. TEG is used as a component in lubricants, contributing to their performance in various applications. TEG plays a role in the formulation of UV-curable resins, which find applications in coatings and adhesives. TEG is employed in the production of materials for electronics and electrical applications.
Storge & Handling
Store in a cool, dry and well-ventilated location away from heat and open flames. Use sealed containers to prevent mositure absorption.
Packing
225KG/Drum