Butyl Acrylate (BA)
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Butyl Acrylate (CAS141-32-2) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Butyl Acrylate
Chemical Name:Butyl Acrylate;BA;CAS 141-32-2
EINECS No.: 205-480-7
Chemical Formula: C7H12O2
Molecular Weight: 128.17
Melting point: -69°C
Boiling point: 61-63℃
Flash point: -63°F
Density at 25°C: 0.894g/mL
Molecular Structure:
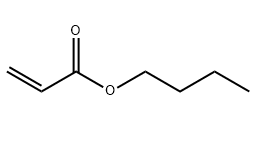
Butyl Acrylate Standard
Appearance: Colourless clear liquid
Content %≥: 99.5
Density at 25°C: 0.894 g/mL
Vapor pressure (20℃): 3.3 mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.410
Application
Butyl acrylate is primarily used as a reactive building block to produce coatings and inks,adhesives, sealants, textiles, plastics and elastomers. Butyl acrylate is used in the following applications:
Adhesives – for use in construction and pressure-sensitive adhesives
Chemical intermediates – for a variety of chemical products
Coatings – for textiles and adhesives, and for surface and water-based coatings, and coatings used for paints, leather finishing and paper
Leather – to produce different finishes, particularly nubuck and suede
Plastics – for the manufacture of a variety of plastics
Textiles – in the manufacture of both woven and non-woven textiles
Storge & Handling
Butyl acrylate is stable under recommended storage conditions. Elevated temperatures can cause hazardous polymerization. Polymerization can be initiated by the absence of air, the presence of free radical initiators and peroxides, or high temperature. The presence of moisture can also accelerate polymerization rate. Butyl acrylate contains inhibitors to minimize polymerization under recommended storage conditions. Maintain inhibitor and dissolved oxygen level. Uninhibited monomer vapors can polymerize and plug relief devices. Avoid unintended contact with activated carbon or silica gel, which may cause polymerization. Avoid contact with clay-based absorbants, and with incompatible materials, such as: Oxidizing materials. Aldehydes, amines, azides, ethers, free radical initiators, halides, mercaptans, mineral acids, peroxides, rust, strong inorganic bases. Metals such as brass or copper.
Packing
200KG/Drum