Isopropanol (IPA)
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Isopropanol (CAS 67-63-0) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Isopropanol
Chemical Name:Isopropanol;CAS 67-63-0
EINECS No.: 200-661-7
Chemical Formula: C3H8O
Molecular Weight: 60.1
Melting point: -89.5°C
Boiling point: 82℃
Flash point: 53°F
Density at 25°C: 0.785 g/mL
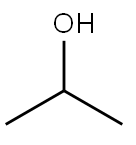
Molecular Structure:
Description
Isopropanol is also known as isopropyl alcohol. It is the simplest secondary alcohol and is one of the isomers of n-propanol. It is a kind of flammable liquid which is colorless with strong smell being similar to the smell of the mixture of ethanol and acetone. It is soluble in water, alcohol, ether, benzene, chloroform and most organic solvents and is miscible with water, alcohol, ether and can form azeotrope with water.
Isopropanol Standard
Appearance: Colourless Liquid
Content %≥: 99.0
Density at 25°C: 0.785 g/mL
Vapor pressure (20℃): 33 mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.377
Explosive limit %(v): 2-13.4
Application
Isopropanol is characterized by its versatile nature, stemming from its ability to act as a solvent, cleaning agent, and disinfectant. This compound boasts a distinctive, mildly sweet odor, and its physical state is that of a clear, colorless liquid. Notably, it exhibits a rapid evaporation rate, leaving minimal residue behind. Isopropanol emerges as a multifaceted compound with a broad spectrum of applications. Its significance extends from industrial processes to everyday cleaning and disinfection, making it a cornerstone in various sectors.
Isopropanol is a powerful solvent that excels in cleaning and degreasing applications. In healthcare environments, maintaining a sterile and sanitized atmosphere is paramount. Isopropanol plays a crucial role in disinfection protocols. Isopropanol is the go-to solution for cleaning electronic components. Its ability to dissolve dirt, dust, and flux residues without introducing moisture makes it a preferred choice. It is used in the cleaning of printed circuit boards (PCBs), connectors, and sensitive electronic devices. Isopropanol is a key ingredient in first aid applications, particularly in the formulation of rubbing alcohol. Its use as a first aid antiseptic involves cleaning wounds and preventing infection. Isopropanol plays a vital role in pharmaceutical manufacturing as a versatile solvent. Its use in the extraction of active pharmaceutical ingredients ensures the production of medications with precise concentrations. Isopropanol serves as a valuable solvent in the ink and coating industry. Its ability to dissolve inks, paints, and coatings makes it an essential component in the formulation of printing inks and coatings. Isopropanol contributes to the stability and consistency of these products, ensuring optimal performance in printing and coating applications. Isopropanol dries out skin to an extent that it is classified as a skin irritant, which is why you shouldn’t use too much of it if you’re using it as an antiseptic. It’s this same effect that makes ispropanol good for muscle ache.It’s often an ingredient in liniments simply because it irritates the skin, and therefore increases blood flow in that part of your body. In turn, this improved blood circulation eases muscle ache and
inflammation. Isopropanol is a common ingredient in nail polish removers. Isopropanol’s low freezing point and ability to melt ice make it a valuable deicing agent, particularly in the aviation industry. Used for deicing aircraft surfaces, isopropanol efficiently removes ice and prevents its formation.
Storge & Handling
Isopropanol should be stored in containers made of materials compatible with its properties. The containers must be tightly sealed to prevent evaporation and potential hazards. Storage areas should be well-ventilated to dissipate any fumes that may accumulate. Adequate ventilation helps reduce the risk of flammability and ensures a safe working environment. Isopropanol should be stored separately from incompatible substances, including strong oxidizers, acids, and bases. Proper segregation helps prevent chemical reactions that may compromise safety.
Packing
160KG/Drum